Datasets: Google Harvest
 Video tutorial available.
Video tutorial available.
Follow the basic steps 1-3 for
creating a new dataset, selecting Google Harvest, and then click Next. The Dataset Wizard window displays:
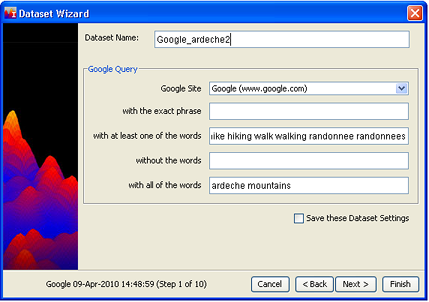
- The default dataset name is the time and date of the Google harvest. You may edit the dataset name.
- From the Google Site drop-down, select which type of Google search you want to make: All of the Web, Google News, or Google Scholar.
- Compose a Google search using the options provided. These will be combined using the Boolean AND, i.e., all conditions must be satisfied for there to be a hit. For example, if you type "hike hiking walk walking" in the field "with
at least one of the words" and type "dog" in the field
"without the words", Google search will look for documents containing
"hike", "hiking", "walk" or "walking" that do not also contain "dog".
To save this search, check Save these Dataset Settings, and click
Next >. The Advanced Google Options panel appears. If you have checked Save these dataset settings, it will be preceded by a dialog that allows you to name the settings. In future, you will be able to repeat the harvest by creating a new dataset with these settings.
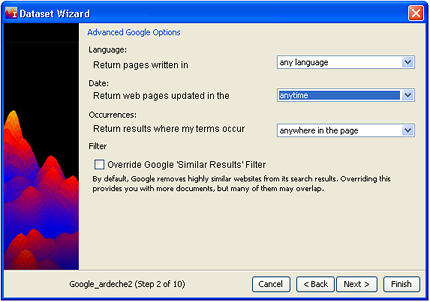
- The defaults for Language, Date, and Occurrences are shown in the
above example. You are not required to change them, although you may want
to hone your query by specifying:
- The language of the pages (specify a single language).
- The period in which pages have been updated (anytime, or within 3 months, 6 months, a year).
- Where the query terms must appear (anywhere, or in the title, in the text, in the URL, or in links).
When you are done, either:
- Click Next and go to step 8. Optional Settings, or
- To start processing using the default settings, go to step 10.
- These settings serve as controls for the duration of a harvest and can be useful if you are experiencing any of the following problems:
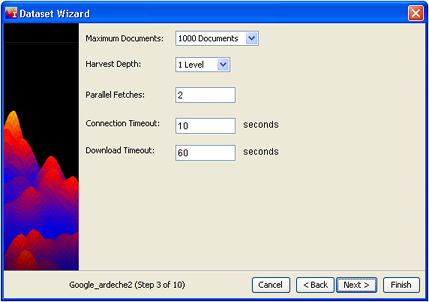
- An excessive number of documents are being retrieved.
Use the Maximum Documents drop-down list to set a reasonable number, and the harvest will be terminated when that number is reached. - The harvest retrieves "linked to" pages that are not relevant to the analysis.
Specify a Harvest Depth of 1 level, which means that links from the top level pages will be followed, but links on those pages will not be. - Harvests seem to take a long time to complete.
Parallel Fetches asks you to specify how many web servers you want to be downloading from at the same time. Clearly, if you have the processor power, having a number of parallel fetches going at once can shorten the harvest time. Attempting too many parallel fetches can actually slow the harvest, however. - Frequent connection timeouts.
Connection Timeout refers to how long the harvester should wait for a reply after it has contacted a web server. If you are experiencing frequent connection timeouts, you may want to increase the timeout interval. - Pages with very large graphics or slow or overloaded servers.
Download Timeout limits how long it may take to actually download a web page, and insures that the harvest will not be stuck trying to fetch a page from a very slow or unresponsive server.
- When you are done, click Next >, and the Filters panel displays.
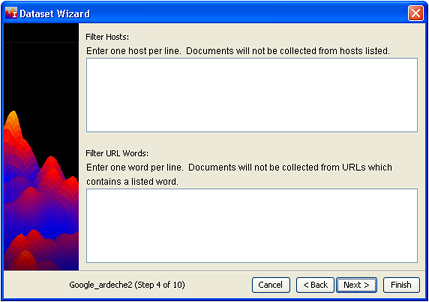
Filters address the following problems:
- Problem: There is a large site which you know contains pages irrelevant to your analysis, that will dominate the harvest and obscure the pages which are most interesting to you.
Solution: You can block that host. A "host" is a web server; its address appears in the URL for a page, immediately after http://. For example, if the URL is http://www.amazon.com/stores/books, the host is "www.amazon.com".
Enter names of hosts you want to avoid in the Filter Hosts box, one per line. - Problem: Your query terms include words which have several meanings, only one of which is interesting for the analysis, or you may want to exclude certain sections of web sites (on-line catalogs, for example).
Solution: If these words can occur in the URLs of sites, you can filter out only those parts of sites that are associated with them. "URL words" are parts of the URL (actually folders on the web server). Documents stored in those folders can be blocked while documents stored outside of them could be retrieved.
- Click Finish to use the default settings for the remainder of the options and start processing immediately.
Start Processing
The Processing dialog opens, informing you that the dataset is being processed. Click OK. The dataset name opens in the list of datasets in the Dataset Editor window. You can monitor its status as it is processed by clicking the Refresh  button at the top of the Dataset Editor window.
button at the top of the Dataset Editor window.
Check the Status of the Google Harvest
While the harvest is ongoing, you can monitor its progress in the Harvest Progress window:
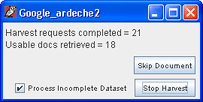
The stages of dataset creation are reflected in the Status column of the Dataset Editor window. To see the complete status details, click the Status  button. The Dataset Details window opens.
button. The Dataset Details window opens.
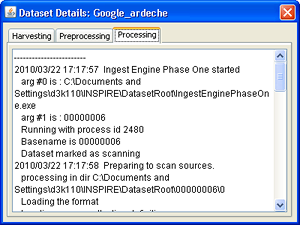
Use the tabs to view status information about the dataset harvesting, preprocessing, and processing phases of the Google harvest. This information can be used to refine your harvest.
![]() Video tutorial available.
Video tutorial available.



 button at the top of the Dataset Editor window.
button at the top of the Dataset Editor window.
 button. The Dataset Details window opens.
button. The Dataset Details window opens. 