You are here: Tools > Search > Search: Basics
Search: Basics
With the Search Tool you can search your dataset for specific words, concepts, or phrases.
Accessing the Search Tool
Click the Advanced  search button on the IN-SPIRE toolbar, or select Tools >
search button on the IN-SPIRE toolbar, or select Tools >  Search. The Search window appears with the Term Search tab on top.
Search. The Search window appears with the Term Search tab on top.
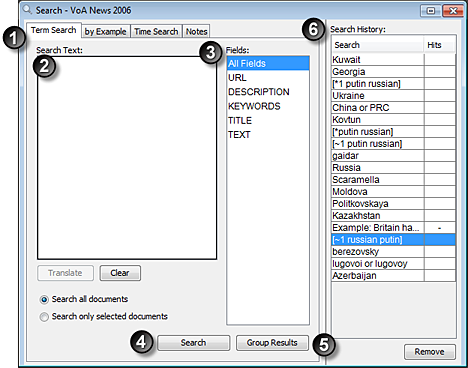
Parts of the Search Window
The numbers following refer to the numbers in the image above.
- One tab for each of the types of searches available. The Term Search panel is uppermost in this image.
- Search Text. What the Search Tool will look for in the documents in the dataset.
- Fields to search. The default is "All Fields," but you can restrict your search to one or more of the fields defined for the dataset.
- Search button. Click Search to launch the search.
- Group Results button. Click Group Results to create a new group containing the hits from the search just completed.
- Search History. A list of all of the searches that have been run on the dataset.
Types of Searches
There are three types of searches: Term Search, By Example, Time Search and Notes.
- Term Search looks for combinations of words. Searches can be constructed using the Boolean operators AND,OR,and NOT. If no Boolean operator is specified, search words are joined with the Boolean AND, with the result that every document in the result set will contain all the search terms. Term Search finds exact matches only. Boolean operators must be capitalized.
- By Example looks for documents having related content rather than for exact word matches. It creates a mathematical signature for the search terms and then looks for documents having a similar signature. The Search Results slider controls the number of hits and how similar the result set documents will be.
- Time Search looks for documents by date. It finds every document associated with the specific date range. This search is also supported in Search Networks.
- Notes looks for matches in the notes attached to documents. Some but not all of the features of Term Search are available (see the Notes tab for which features are supported).
See Types of Searches for information on using the four types of searches, and term search syntax.
Creating a Group from Search Results
The current selection, for example the results of a search, will always appear as a locked group in the Groups Selection History folder located in the right sidebar. These Selection History groups are not permanent, however. Only the four most recent selections will be available.
To create a permanent group from the results of a search, click the Group Results button. By default, the new group will have the same name as the search, preceded by a letter showing the type of search that found those particular documents.
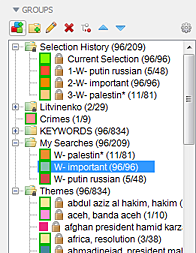
Using the Search History
Searches are automatically saved in the Search History. If a dataset has been edited, all of the searches performed on it will be listed but there will be no Hits listed, since the composition of the dataset may have changed since the search was run. To see the hits, you will need to run the searches again. Select one in the Search History list and click Search.
The Search History panel of the Search window contains a list of all the searches that have been run on the dataset. It shows the type of search and the number of document hits the search produced.
- No prefix indicates a Term Search
- "Example:" indicates a Search by Example
- "Note:" indicates a Search within Notes
- "Field:" indicates a search on a Field such as Title, rather than All Fields.
You can rerun a search at any time by selecting it from the list and
clicking the Search button.
Editing Searches from the Search History
A Term Search, which searches all fields by default, may have returned some analytically meaningless hits. You may be able to eliminate these by editing the search to point at a particular field or fields. To edit and rerun a search:
- Click on a search in the Search History list.
- Click on one or more of the Field Types.
- Click Search.
Deleting a Search from the Search History
- In the Search History list, click on the search you want to delete.
- Click Remove. The search will be removed from the list in Search History.
Translating Searches
If you have a translation engine installed on your system or server, and if you enabled languaged detection when you created your dataset, you can use the integrated translation capabilities of IN-SPIRE to formulate bilingual searches. To search a bilingual dataset:
- From the main menubar, choose Translation > Translator Settings. The Translator Settings window opens.
- You can choose to translate documents and/or queries (searches). Which translation capabilities are available depends on which translators are installed on your system. The languages you choose here will control which how searches run from the Search Tool will be translated. Click Translate to apply these settings. The Translator Settings window closes.
- Open Search. The Translate button on the Search window will now be active.
- Enter search terms in the Search Text box. For example, for a dataset containing French documents, to search for "terrorist", type "terrorist" in the Search Text field.
- Click the Translate button. The search term(s) will be translated and both English and foreign language terms will appear. In this example, we see "terrorist" or "terroriste".
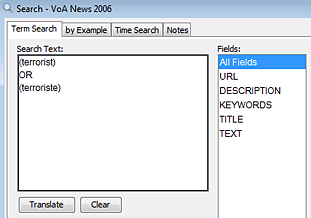
- Click the Search button. Search will find documents containing either the English term or the foreign language term.
 Search. The Search window appears with the Term Search tab on top.
Search. The Search window appears with the Term Search tab on top. ![]() search button on the IN-SPIRE toolbar, or select Tools >
search button on the IN-SPIRE toolbar, or select Tools >  Search. The Search window appears with the Term Search tab on top.
Search. The Search window appears with the Term Search tab on top. 

