Data Sets
Overview
Creating New
--ASCII Text
--XML
--Google Harvest
--Web Harvest
Settings
--Fields
--Stopwords
--Stopmajors
--Punctuation Rules
Editing
Merging
Exporting
Importing
Subsetting
Visualizations
Galaxy
--Basics
--Outliers
ThemeView
Settings
Tools
Document Viewer
Gist
Groups
--Basics
--Evidence Panel
Major Terms
Queries
Print
Probe
Time Slicer
About version 2.2
Overview
Known issues
![]()
Data Sets: Google Harvest
Follow the Basic Steps 1. and 2 listed in Creating a Data Set. The following screen appears:
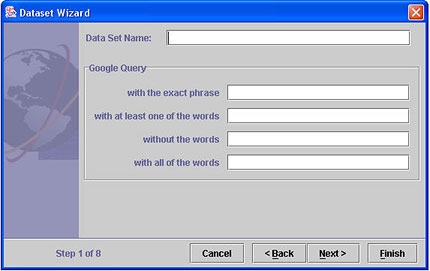
- Enter a data set name.
- Type in the query text, in one or more of the Google Query boxes. The query will AND the options together. For example, if you type "cat" in "with at least one of the words" and type "dog" in the box "without the words", Google search will look for documents containing "cat" that do not also contain "dog".Finally, click Next>. The Advanced Google Options panel appears.
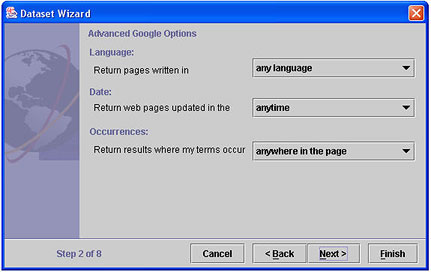
- The defaults for Language, Date, and Occurrences are shown in the
above screenshot. You are not required to change them, although you
may wish to hone your query by specifying:
- The language of the pages (any language, or specify a single language).
- The period in which pages have been updated (anytime, or within 3 months, 6 months, a year)
- Where the query terms must appear (anywhere, or in the title, in the text, in the URL, or in links).
When you're done, click Next> and go to Step 4, or to accept the defaults on the following screens and start processing, click Finish and go to Step 6.
- The settings on this screen serve as controls for the duration of a harvest and can be useful if you are experiencing any of the following problems:
- An excessive number of documents is being retrieved.
Use the Maximum Documents dropdown to set a reasonable number, and the harvest will be terminated when that number is reached. - The harvest retrieves "linked to" pages that are not relevant
to the analysis
Specify a Harvest Depth of 1 level, which means that links from the top level pages will be followed, but links on those pages will not be. - Harvests seem to take a long time to complete
Parallel Fetches asks you to specify how many web servers you want to be downloading from at the same time. Clearly, if you have the processor power, having a number of parallel fetches going at once can shorten the harvest time. Attempting too many parallel fetches can actually slow the harvest, however. - Frequent connection timeouts
Connection Timeout refers to how long the harvester should wait for a reply after it has contacted a web server. If you are experiencing frequent connection timeouts, you may want to increase the timeout interval. - Pages with very large graphics or slow or overloaded servers
Download Timeout limits how long it may take to actually download a web page, and insures that the harvest won't get stuck trying to fetch a page from a very slow or unresponsive server.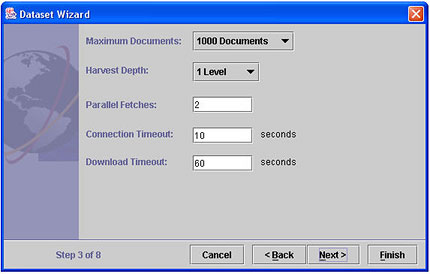
When you are done, click Next> and go to Step 5, or to accept the default settings for Filters as well as Stopwords, Punctuation, and Stopmajor words, go to Step 6.
- The Filters panel appears.
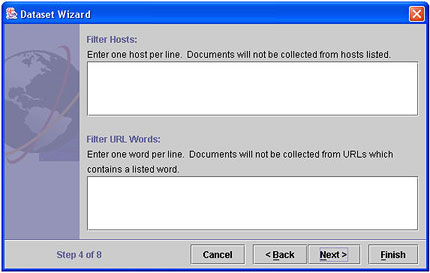
Filters help you to deal with the following problems:
- A large site which you know contains pages that are not relevant
to your analysis will dominate the harvest and obscure the pages
which are most interesting to you.
A "host" is a web server; its address appears in the URL for a page, immediately after http://. For example, if the URL is http://www.amazon.com/stores/books, the host is "www.amazon.com". Enter names of hosts you want to avoid in the Filter Hosts box, one per line. - Your query terms include words which have several meanings, only one of which is interesting for the analysis, or you may want to exclude certain sections of web sites (on-line catalogs, for example).
Enter hosts or URL words to filter and click Next> and go to Optional Settings or to use the default settings for the remainder of the options and start processing immediately, click Finish and go to Step 6.
- A large site which you know contains pages that are not relevant
to your analysis will dominate the harvest and obscure the pages
which are most interesting to you.
-
Start Processing
The Processing dialog opens, informing you that the data set is being processed. Click OK. The data set appears in the list of data sets in the Data Set Editor window. You can monitor its status as it is processed by clicking
 ,
the Refresh button, at the top of the Data Set Editor window.
,
the Refresh button, at the top of the Data Set Editor window. -
Control the Harvest While it is Running
The progress of the harvest is reflected in the Harvest Progress window:
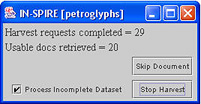
Harvest requests completed is the number of requests the harvester has made and completed; this number will not be the same as the number of Usable docs retrieved. There are several reasons why a request does not result in a usable document:- The request failed (not found, nothing was returned, or the request timed out).
- The page contains only links to other pages
- The page is not decipherable (unexpected data format, for example)
- The page is missing specific required tags (at certain custom search sites such as FBIS)
All requests that result in unusable data are logged in the HarvestLog.txt file, which can be found here: INSPIRE_HOME\DatasetRoot\Harvest\HarvestLog.txt. The default location for INSPIRE_HOME is C:\\Program Files\INSPIRE
- If the harvester appears to be "stuck", force the harvest to move on by clicking Skip Document.
- If the harvest is proceeding very slowly and the number of usable documents retrieved is sufficient for a visualization, make sure the Process Incomplete Dataset checkbox is selected (checked), and click Stop Harvest. The process of developing a visualization continues, and when it completes, a Galaxy will be available for the documents that have been harvested.
- If the harvest is returning very few usable documents and you would
like to revise the URL list or other harvest settings, uncheck the
Process Incomplete Dataset checkbox, and click Stop Harvest.
The harvest stops and no visualization is developed for the documents
already harvested.